Fully Guided and Minimally Invasive Implant Placement as the Basis for Effective Digital Fabrication of a Tapered-Crown Full-Arch Prosthesis - Clinical Case Report - Home
Clinical Case Report
Fully Guided and Minimally Invasive Implant Placement as the Basis for Effective Digital Fabrication of a Tapered-Crown Full-Arch Prosthesis
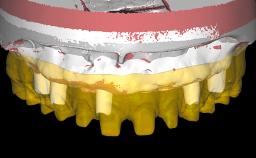
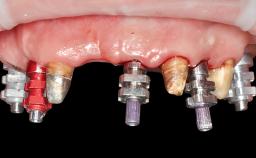
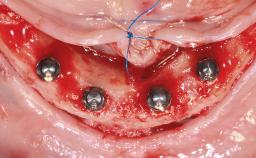
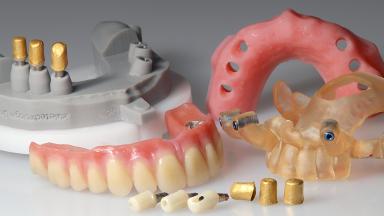
A 74-year-old male patient presented to the Department of Oral Medicine at the Goethe University in Frankfurt, Germany. The patient had been edentulous for 15 months and had been treated with a complete denture by students in the undergraduate program. During a recall appointment, the patient complained of poor retention of his maxillary complete denture. The prosthetic site consisted of a rigid and thick maxillary ridge with an undercut in the left posterior region. The prosthesis covered the entire palate and was dislodged by biting on solid foods such as apples. The patient did not have high esthetic expectations, but he did want improved chewing comfort and "fixed teeth".
- Surgical classification
- Complex
- Prosthodontic classification
- Complex
- Source
- Treatment Guide 15
- Purchase price
- 10 Academy Coins
- CPD/CME
- 25 hours
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code