
Combined SFE and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation with Autologous Block Grafts, BCP, and GBR using a Staged Approach - Clinical Case Report - Home
Clinical Case Report
Combined SFE and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation with Autologous Block Grafts, BCP, and GBR using a Staged Approach
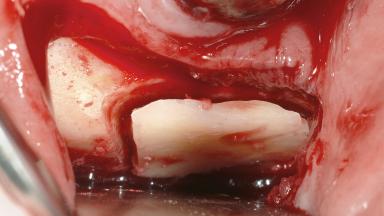
Various patterns of alveolar bone resorption are known to occur in the posterior maxilla. Following tooth loss, resorption may take a buccopalatal direction, resulting in a narrow ridge displaced toward the palate. Resorption may also proceed vertically in an apical direction, reducing the vertical dimension of the ridge and increasing the interocclusal space. Another common pattern of atrophy is caused by volume increases of the maxillary sinus, which will reduce the residual bone volume in an occlusal direction due to downward displacement of the sinus floor. Most cases are characterized by combined defects, leading to a variety of atrophy configurations. Whenever there is a greater need for augmentation than elevating the sinus floor with an inlay bone graft, horizontal and vertical augmentation of the residual ridge may be accomplished by intraoral harvesting of autologous onlay block grafts in the same surgical procedure. We refer to this procedure as “inlay-onlay” grafting of the posterior maxilla.
- Surgical SAC classification
- Complex
- Prosthodontic SAC classification
- Straightforward
- Source
- Treatment Guide 5
- Purchase price
- 10 Academy Coins
- CPD/CME
- 0.25 hours
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code


