Rehabilitating an Edentulous Maxilla with Three Separate Bridges - Clinical Case Report - Home
Clinical Case Report
Rehabilitating an Edentulous Maxilla with Three Separate Bridges
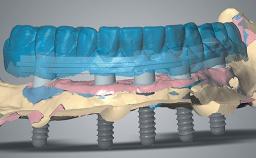
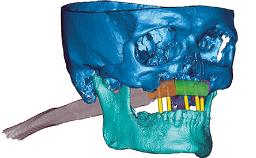
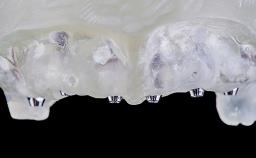
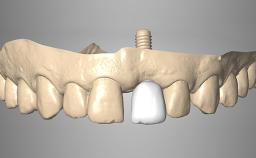
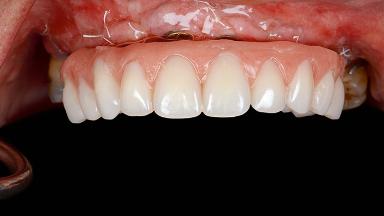
A 55-year-old woman was referred to our clinic for implant therapy. She was healthy and had stopped smoking two years previously. Ten years before, the patient had received extensive dental treatment in both jaws. The patient reported that her dental condition had deteriorated progressively since that time. At the time of presentation, the maxillary bridge was loose. The clinical and radiographic examinations revealed a highly compromised situation for all the teeth that supported the bridge and for other teeth.
- Surgical SAC classification
- Complex
- Prosthodontic SAC classification
- Complex
- Source
- Treatment Guide 11
- Purchase price
- 10 Academy Coins
- CPD/CME
- 0.25 hours
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code