Rehabilitating an Edentulous Maxilla with a Fixed Dental Prosthesis Using a DSD-Guided Approach - Clinical Case Report - Home
Clinical Case Report
Rehabilitating an Edentulous Maxilla with a Fixed Dental Prosthesis Using a DSD-Guided Approach
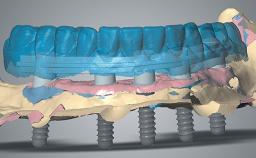
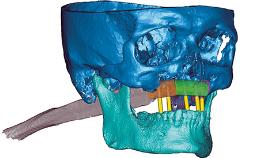
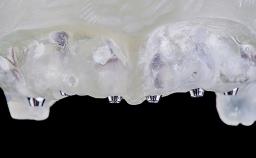
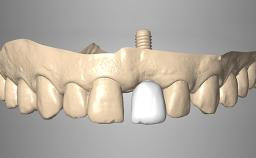
A 60-year-old man was referred to the Center of Excellence for Prosthodontics and Implant Dentistry (CEPI) of the School of Dentistry of the University of São Paulo, Brazil for implant therapy. Anamnesis, clinical examination, and radiographs revealed esthetic and functional problems, the absence or structural compromise of various teeth (16–11, 21, 22, 24, 25, 37, 45, and 48), periodontal and endodontic problems (17 and 27), implant fracture (46), and occlusal disorders . The patient reported that he was undergoing treatment for cardiovascular diseases.
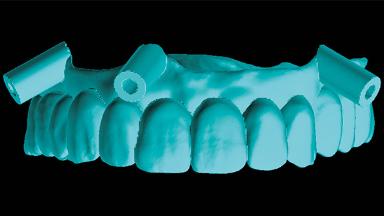
- Surgical SAC classification
- Advanced
- Prosthodontic SAC classification
- Complex
- Source
- Treatment Guide 11
- Purchase price
- 10 Academy Coins
- CPD/CME
- 0.25 hours
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code