Iatrogenic Complications Managed by Replacing Prosthetic Components: Non-surgical Approach - Clinical Case Report - Home
Clinical Case Report
Iatrogenic Complications Managed by Replacing Prosthetic Components: Non-surgical Approach
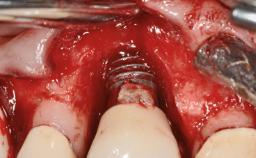
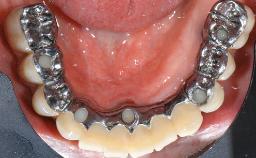
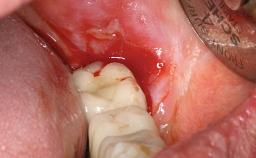
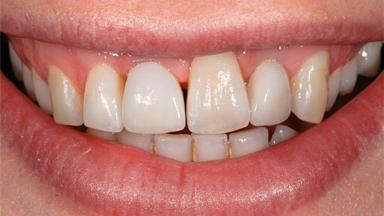
A male patient had lost teeth 11 and 22 as a result of a bicycle accident at age 14. In his adolescent years, a removable prosthesis had replaced the missing teeth. At age 21, the patient was referred by his dentist to the university clinic for treatment of the missing teeth 11 and 22 with implants. He was in good health and a nonsmoker. The absence of teeth 11 and 22 over many years had led to significant atrophy of the alveolar ridge, particularly at site 11. As a first step, the alveolar ridge was augmented using a block graft to replace the lost bone. A Straumann SP implant (diameter 4.1 mm, length 12 mm; Institut Straumann AG, Basel, Switzerland) and a Straumann Narrow Neck implant (length 10 mm) were inserted in the correct location and axial position at sites 11 and 22, respectively, six months later. After three months of healing and subsequent reentry, the patient returned to the referring dentist to receive the prosthetic restoration. The patient was seen again six months after the restoration had been placed. The frontal view showed a high smile line, an irregular gingival profile, and a bluish-gray tinge to implant crowns 11 and 22 compared to the natural dentition.
- Surgical SAC classification
- Complex
- Prosthodontic SAC classification
- Advanced
- Source
- Treatment Guide 8
- Purchase price
- 10 Academy Coins
- CPD/CME
- 0.25 hours
Share this page
Download the QR code with a link to this page and use it in your presentations or share it on social media.
Download QR code